 |
Professor Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Service de Chimie Physique et Biologie Théorique Faculté des Sciences Campus Plaine, C.P. 231 Université libre de Bruxelles, 1050 Brussels, Belgium ☎ +32 (0)2 650 5699 📠 +32 (0)2 650 5767 ✉ laurence.rongy@ulb.be |
- Licence en Sciences Chimiques (Ms in Chemistry), Université libre de Bruxelles, 2004
- Doctorat en Sciences Chimiques (PhD in Chemistry), Université libre de Bruxelles, 2008
- Postdoc School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard, 2008-2009
- Postdoc Dept Chemical Engineering, Yale University, 2009-2010
Les sujets de mémoire de cette année se trouvent dans ce document PDF.
Nonlinear chemistry
Multicomponent diffusion
Reaction-diffusion-convection dynamics
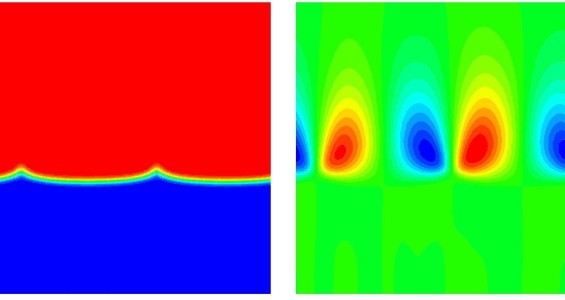
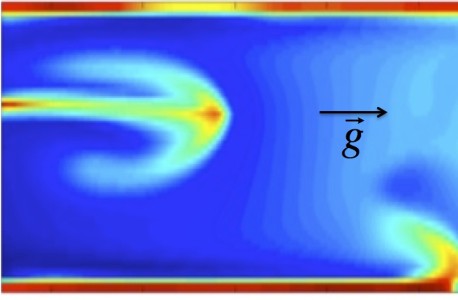
Due to concentration and temperature differences across an exothermic autocatalytic traveling front, Rayleigh-Taylor or double-diffusive instabilities can develop when the front travels in a Hele-Shaw cell oriented vertically in the gravity field. In thin layers of solution in contact with air, surface tension effects can in addition come into play. Our research aims at a theoretical understanding of the spatio-temporal dynamics resulting from the coupling between these various hydrodynamic instabilities with the autocatalytic reactions.
 |
 |
| Deformation
of a chemical front featuring light and hot products in red
invading downwards heavy and cold products in blue. Chemical
reactions are able to destabilize statistically stable
density stratifications (PRL 96, 154401 (2006)) (left:
concentration field; right: stream function) |
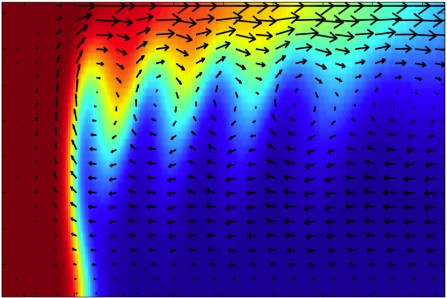
Marangoni-driven
flow around an autocatalytic chemical front traveling in a horizontal liquid layer with a free surface |
Out-of-equilibrium
nonideal systems
PIONEER: Physico-chemistry in out-of-equilibrium nonideal environments and spatially extended reactive systems
PIONEER: Physico-chemistry in out-of-equilibrium nonideal environments and spatially extended reactive systems
The theme of the project is the modeling of reactive and transport processes in out-of-equilibrium nonideal environments. The strong intermolecular interactions characterizing such systems play an important role in numerous chemical, environmental, and biological phenomena. The first part of the project will focus on transport phenomena, such as multicomponent diffusion in two-phase systems (e.g. liquid-gas) and the natural convection induced by unstable density gradients in the gravity field. With the help of optimization techniques and in close collaboration with experiments, this modeling approach will allow measuring diffusion coefficients in nonideal mixtures. Those values are, indeed, crucial to describe many engineering and environmental processes such as the underground transport of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the context of enhanced oil recovery or carbon sequestration. In the second part, reactive systems will be considered. We will derive a reaction-diffusion-convection model for two-phase nonideal systems in the context of carbon sequestration or reactive interfaces. Nonidealities will be taken into account in the reaction kinetics through empirical activity coefficients as a first step. A second step will consist in establishing an expression for the free energy of the system including intermolecular interactions.
See also: http://www.ulb.ac.be/recherche/presentation/fr-arcrongy.html
- A. Bigaj, M. A. Budroni, L. Rongy
Influence of chemo-hydrodynamical oscillations in bimolecular reactions on mixing, ChemSystemsChem, e202400099 (2025). - S. Kabbadj, L. Rongy, A. De Wit, A. Woods
Effect of a bimolecular chemical reaction on the convective dissolution of CO2, Proceedings of the MATRIX Research Program: Instabilities of Flows in Porous Media, (2025). - A. Bigaj, M. A. Budroni, L. Rongy
Exploring buoyancy-driven effects in chemo-hydrodynamic oscillations sustained by bimolecular reactions, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 27, 1008 (2025). - K. Wüthrich, B.L. Feringa, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Chemistry Challenges of the 21st Century: 100 Years of Solvay Conferences, Proceedings of the 26th Solvay conference on Chemistry, World Scientific (2024). - D. Bistri, I. Arretche, J.J. Lessard, M. Zakoworotny, S. Vyas,
L. Rongy, R. Gomez-Bombarelli, J.S. Moore, P. Geubelle
A mechanism-based reaction-diffusion model for accelerated discovery of thermoset resins frontally polymerized by olefin metathesis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 21877 (2024). - J. Gillet, Y. Geerts, L. Rongy, Y. De Decker
Differences in enantiomeric diffusion can lead to selective chiral amplification, PNAS 121, e2319770121 (2024). - A. Bigaj, V. Upadhyay, L. Rongy
Thermal effects on chemically induced Marangoni convection around A + B → C reaction fronts, J. chem. Phys. 160, 064705 (2024). - S. Kabbadj, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Effect of variable solubility on reactive dissolution in partially miscible systems, Phys. Rev. E 107, 065109 (2023). - A. Bigaj, M. A. Budroni, D. M. Escala, L. Rongy
Marangoni- vs. buoyancy-driven flows: competition for spatio-temporal oscillations in A + B -> C systems, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 11707 (2023). - R. Tiani, L. Rongy
Marangoni-driven nonlinear dynamics of bimolecular frontal systems: a general classification for equal diffusion coefficients, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 381, 20220080 (2023). - J. Gillet, L. Rongy, Y. De Decker
Spontaneous mirror symmetry breaking in reaction–diffusion systems: ambivalent role of the achiral precursor, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24, 26144 (2022). - R. Tiani, J. A. Pojman, L. Rongy
Critical Role of Layer Thickness in Frontal Polymerization , J. Phys. Chem. B 126, 3607 (2022). - R. Tiani, L. Rongy
Spatial and Temporal Oscillations of Surface Tension Induced by an A + B → C Traveling Front, Front. Phys. 10, 860419 (2022). - M. A. Budroni, F. Rossi, L. Rongy
From Transport Phenomena to Systems Chemistry: Chemohydrodynamic Oscillations in A + B → C Systems, ChemSystemsChem 3, e2100023 (2021). - M. Jotkar, A. De Wit, L. Rongy
Control of chemically driven convective dissolution by differential diffusion effects, Phys. Rev. Fluids 6, 053504 (2021). - M. A. Budroni, A. Polo, V. Upadhyay, A. Bigaj, L. Rongy
Chemo-hydrodynamic pulsations in simple batch A + B → C systems, J. Chem. Phys. 154, 114501 (2021). - A. De Wit, L. Rongy
Séquestration géologique du CO2 : la chimie au service de l’environnement, L’Artichaut 38, 8 (2020). - M. Jotkar, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Reactive convective dissolution with differential diffusivities: Nonlinear simulations of onset times and asymptotic fluxes, Phys. Rev. Fluids 5, 104502 (2020). - A. Grau Ribes, Y. De Decker, L. Rongy
Connecting gene expression to cellular movement: A transport model for cell migration, Phys. Rev. E 100, 032412 (2019). - R. Tiani and L. Rongy
Complex dynamics of interacting fronts in a simple A + B → C reaction-diffusion system, Phys. Rev. E 100, 030201(R) (2019). - M. Jotkar, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Chemically-driven convective dissolution, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 19054 (2019). - M. A. Budroni, V. Upadhyay, L. Rongy
Making a Simple A + B → C Reaction Oscillate by Coupling to Hydrodynamic Effect, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 244502 (2019).
Cover - M. Jotkar, A. De Wit, L. Rongy
Enhanced convective dissolution due to an A + B → C reaction: control of the non-linear dynamics via solutal density contributions, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 6432 (2019). - V. Loodts, H. Saghou, B. Knaepen, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Differential Diffusivity Effects in Reactive Convective Dissolution, Fluids 3, 83 (2018). - P. Bába, L. Rongy, A. De Wit, M. J. B. Hauser, Á. Tóth, D.
Horváth
Interaction of Pure Marangoni Convection with a Propagating Reactive Interface under Microgravity, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 024501 (2018). - R. Tiani, A. De Wit and L. Rongy
Surface tension-and buoyancy-driven flows across horizontally propagating chemical fronts, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 225, 76 (2018). - V. Loodts, C. Thomas, L. Rongy and A. De Wit
Dissolution-driven convection in reactive systems, Chimie nouvelle 126, 1 (2017). - A. Grau Ribes, Y. De Decker, C. Gérard and L. Rongy
Modelling the propagation of a dynamical signature in gene expression mediated by the transport of extracellular microRNAs, Mol. BioSyst. 13, 2379 (2017). - V. Loodts, B. Knaepen, L. Rongy a and A. De Wit
Enhanced steady-state dissolution flux in reactive convective dissolution, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 18565 (2017). - C. Thomas, V. Loodts, L. Rongy and A. De Wit
Convective dissolution of CO2 in reactive alkaline solutions: Active role of spectator ions, Int. J. of Greenhouse Gas Control 53, 230 (2016). - R. Tiani and L. Rongy
Influence of Marangoni flows on the dynamics of isothermal A + B → C reaction fronts, J. Chem. Phys. 145, 124701 (2016). - V. Loodts, P.M.J. Trevelyan, L. Rongy, and A. De Wit
Density profiles around A + B → C reaction-diffusion fronts in partially miscible systems: A general classification, Phys. Rev. E 94, 043115 (2016). - V. Loodts, L. Rongy and A. De Wit
Chemical control of dissolution-driven convection in partially miscible systems: Theoretical classification, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 29814 (2015). - Z. Zheng, L. Rongy and H.A. Stone
Viscous fluid injection into a confined channel, Phys. Fluids 27, 062105 (2015). - D. Horvath, M.A. Budroni, P. Baba, L. Rongy, A. De Wit, K.
Eckert, M.J.B. Hauser, A. Toth
Convective dynamics of traveling autocatalytic fronts in a modulated gravity field, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 26279 (2014). - V. Loodts, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Impact of pressure, salt concentration, and temperature on the convective dissolution of carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions, Chaos 24, 043120 (2014). - V. Loodts, C. Thomas, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Control of Convective Dissolution by Chemical Reactions: General Classification and Application to CO2 Dissolution in Reactive Aqueous Solutions, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 114501 (2014). - L. Rongy, K.B. Haugen, A. Firoozabadi
Mixing from Fickian diffusion and natural convection in binary non-equilibrium fluid phases, AIChE Journal 58, 1336-1345 (2012). - M.A. Budroni, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Dynamics due to combined buoyancy- and Marangoni-driven convective flows around autocatalytic fronts, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 14619-14629 (2012). - L. Rongy, P. Assemat, A. De Wit
Marangoni-driven convection around exothermic autocatalytic chemical fronts in free-surface solution layers, Chaos 22, 037106 (2012). - K. Eckert, L. Rongy, A. De Wit
A + B → C reaction fronts in Hele-Shaw cells under modulated gravitational acceleration, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 7337-7345 (2012). - L. Rongy, P.M.J. Trevelyan, A. De Wit
Influence of buoyancy-driven convection on the dynamics of A+B → C reaction fronts in horizontal solution layers, Chem. Eng. Sci. 65, 2382-2391 (2010). - L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Buoyancy-driven convection around exothermic autocatalytic chemical fronts traveling horizontally in covered thin solution layers, J. Chem. Phys. 131, 184701 (2009). - L. Rongy, G. Schuszter, Z. Sinkó, T. Tóth, D. Horváth, A. Tóth,
A. De Wit
Influence of thermal effects on buoyancy-driven convection around autocatalytic chemical fronts propagating horizontally, Chaos 19, 023110 (2009). - L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Solitary Marangoni-driven convective structures in bistable chemical systems, Phys. Rev. E 77, 046310 (2008). - L. Rongy, A. De Wit, G.M. Homsy
Asymptotic structure of steady nonlinear reaction-diffusion-Marangoni convection fronts, Phys. Fluids 20, 0721103 (2008). - L. Rongy, P.M.J. Trevelyan, A. De Wit
Dynamics of A+B → C reaction fronts in the presence of buoyancy-driven convection, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 084503 (2008). - L. Rongy
Influence of Marangoni and buoyancy convection on the propagation of reaction-diffusion fronts, PhD Thesis, ULB (2008). - L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Steady convective flows traveling with chemical fronts, Chimie Nouvelle 96, 106 (2007). - L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Marangoni flow around chemical fronts traveling in thin solution layers: influence of the liquid depth, J. Eng. Math. 59, 221-227 (2007). - L. Rongy, N. Goyal, E. Meiburg, A. De Wit
Buoyancy-driven convection around chemical fronts traveling in covered horizontal solution layers, J. Chem. Phys. 127, 114710 (2007). - L. Rongy, A. De Wit
Steady Marangoni flow traveling with a chemical front, J. Chem. Phys. 124, 164705 (2006).
